Embedded Linux on the ESP32-S3
This is a newbies guide to Embedded Linux on the ESP32-S3. Still actively WIP.
Yes, you read that correctly: Linux on the ESP32-S3!! Way cool. Some may even call this the dawn of a new era.
If you are experienced at building Linux kernels, you may wish to simply just head to jcmvbkbc’s instructions at wiki.osll.ru or ESP32DE/Boot-Linux-ESP32S3-Playground.
For even fewer details and no instructions, there’s a jcmvbkbc rebuild-esp32s3-linux.sh gist script, and my fork of it, just in case the upstream is removed.
This particular flavor of Linux leverages the BusyBox Software Suite.
Me, I’m a Windows developer at the day job with a part time consulting gig at wolfSL. Most of my Linux activity these days is on WSL, not a “real” Linux box. I needed some assistance on building a Linux kernel, particularly for an embedded device. Big thanks to eMbeddedHome that helped me, and credit jcmvbkbc for the impressive but humbly announced work on Open Source & Linux Lab.
There are some additional tidbits of technical details in jcmvbkbc/linux-xtensa #5
Overview
| Toolchain | Name |
|---|---|
| Architecture | Xtensa |
| SoC | ESP32-S3 |
| Minimum RAM | 8MB (PSRAM, the -R8) |
| Minimum Flash | 8MB (-N8) |
| Name | xtensa-esp32s3-linux-uclibcfdpic |
| Base directory | /mnt/s3liux |
| Host disk | 100GB free (observed ~5GB upon completion) |
Upon completion of building toolchain there should be a directory structure that looks like this:
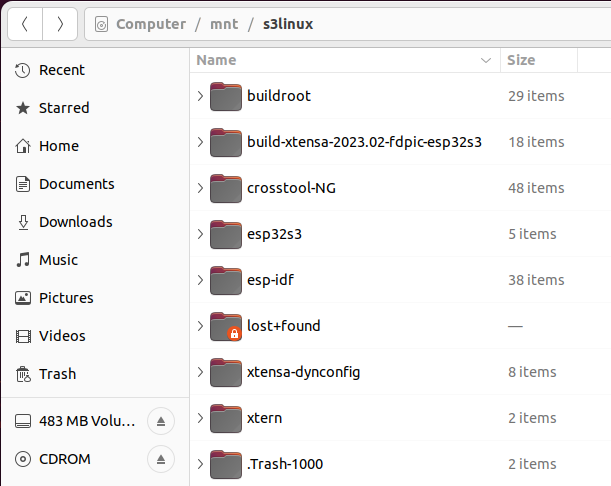
Requirements
These instructions are based on a Windows 11 machine with VMware workstation running Ubuntu 22.04 (Jammy Jellyfish).
The particular VM used here has rather modest specs: 4 processor, 4GB RAM, 60GB main disk, 100GB s3linux disk.
To share files between Linux and the Windows host, see the VMware docs.
Here there’s a local local c:\test folder shared in VMware as test:
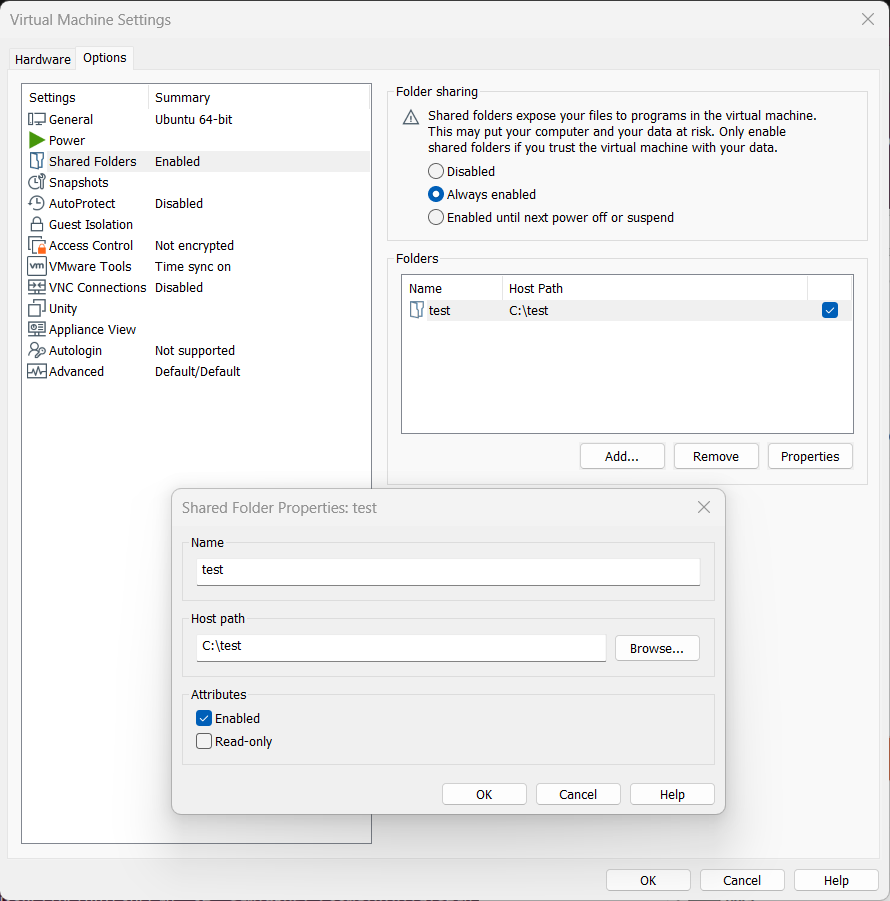
To enable the C:\test\ directory to be in /mnt/c/test/:
/usr/bin/vmhgfs-fuse .host:/test /mnt/c/test -o subtype=vmhgfs-fuse
Tips
Some of the many tips I learned from rudi ;-) @eMbeddedHome
- 120MHz only works with Quad and quad is only supported <=16 from esptool
- you have to write FF ‘s by self if you want erase-flash cause esptool does not support all flash commands > 32MB. See esptool #883
Hardware
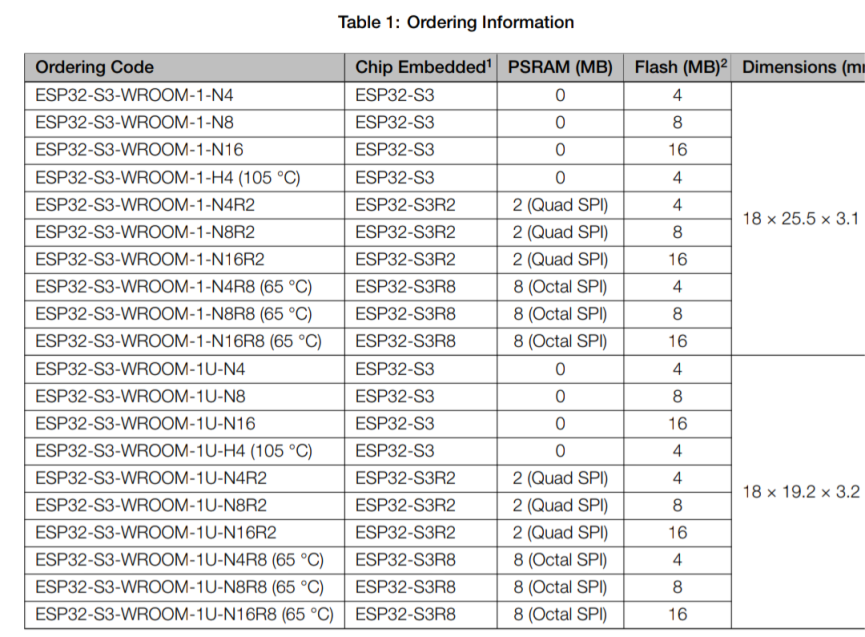
Key to this exercise is enough memory on an ESP32-S3: both Flash and PSRAM. Minimum requirements:
8MB Flash
8MB PSRAM
If you are unsure about which products have which amounts of memory: the -N is Flash, and the -R is PSRAM
System prep
Be sure to have some sort of terminal program ready, and
not just the idf-monitor.
The idf.py monitor does not work so well with an interactive Linux login prompt.
Putty on Windows is one possible option.
Next: dependencies. They are not very intuitively named
and give errors one at a time. Using apt-mark showmanual, these are the packages installed on my Ubuntu VM:
sudo apt-get install \
autoconf \
automake \
base-passwd \
bison \
bsdutils \
build-essential \
ccache \
clang \
cmake \
dash \
dfu-util \
diffutils \
efibootmgr \
findutils \
flex \
fonts-indic \
gawk \
git \
gperf \
grep \
grub-common \
grub-efi-amd64-bin \
grub-efi-amd64-signed \
grub-gfxpayload-lists \
grub-pc \
grub-pc-bin \
grub2-common \
gzip \
help2man \
hostname \
init \
language-pack-en \
language-pack-en-base \
language-pack-gnome-en \
language-pack-gnome-en-base \
libdebconfclient0 \
libffi-dev \
libflashrom1 \
libftdi1-2 \
libllvm13 \
libssl-dev \
libtool \
libtool-bin \
libusb-1.0-0 \
linux-generic-hwe-22.04 \
login \
make \
mokutil \
ncurses-base \
ncurses-bin \
ninja-build \
open-vm-tools-desktop \
os-prober \
python3 \
python3-pip \
python3-venv \
sed \
shim-signed \
texinfo \
ubuntu-desktop \
ubuntu-desktop-minimal \
ubuntu-minimal \
ubuntu-standard \
ubuntu-wallpapers \
wget
Setup 100GB disk
It’s never cool to be running a long build process and run out of disk space.
These instructions should work on WSL, but in this first run I setup a 100GB disk on VMware for Windows:
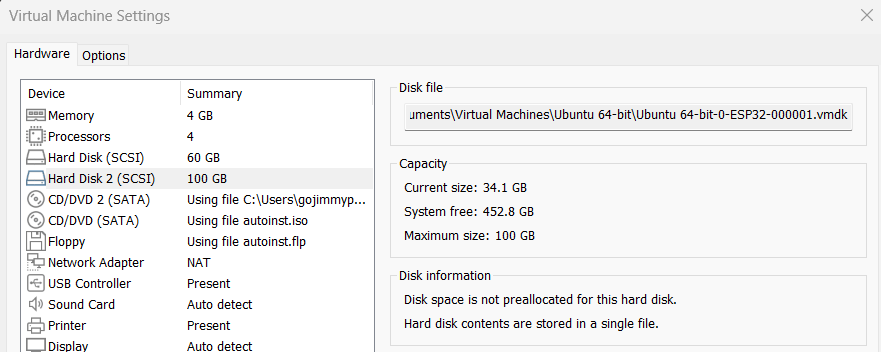
Use the fdisk command to configure a new disk. All the defaults, here as /dev/sdb1:
Device Start End Sectors Size Type
/dev/sda1 2048 4095 2048 1M BIOS boot
/dev/sda2 4096 1054719 1050624 513M EFI System
/dev/sda3 1054720 125827071 124772352 59,5G Linux filesystem
Disk /dev/sdb: 100 GiB, 107374182400 bytes, 209715200 sectors
Disk model: VMware Virtual S
Units: sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
Disklabel type: dos
Disk identifier: 0x[..]
Device Boot Start End Sectors Size Id Type
/dev/sdb1 2048 209715199 209713152 100G 83 Linux
In my case, I mounted it in /mnt/:
sudo fdisk --list
mkdir /mnt/s3linux
sudo mount /dev/sdb1 /mnt/s3linux
Note that if you want to share a drive in an Ubuntu VM with the Windows filesystem, the c drive
could also be mapped in /mnt/, giving the same path as if on WSL.
CT_PREFIX=pwd/builds nice ./ct-ng menuconfig
Using the instructions from jcmvbkbc
Build toolchain dynconfig library and export XTENSA_GNU_CONFIG for use by the toolchain
git clone https://github.com/jcmvbkbc/xtensa-dynconfig -b original
git clone https://github.com/jcmvbkbc/config-esp32s3 esp32s3
make -C xtensa-dynconfig ORIG=1 CONF_DIR=`pwd` esp32s3.so
export XTENSA_GNU_CONFIG=`pwd`/xtensa-dynconfig/esp32s3.so # make sure this environment variable is set for all commands involving building or using the toolchain
Configure the toolchain
The ct-ng tool (aka “crosstool-ng”, see docs) is the
toolchain building system. Here we build the compiler, linker, etc… for taking local source
code and creating a binary that will run on our target, in this case to Xtensa on the ESP32-S3.
There’s an optional CT_PREFIX=pwd/builds nice ./ct-ng menuconfig command that is quite helpful.
Download and make crosstool-ng
(note there are also steps on the instructions from jcmvbkbc for building the toolchain manually)

# in this example, the toolchain is installed in the /mnt/s3linux directory
cd /mnt/s3linux
git clone https://github.com/jcmvbkbc/crosstool-NG.git -b xtensa-fdpic
pushd crosstool-NG
./bootstrap && ./configure --enable-local && make
# Optional menuconfig
# CT_PREFIX=`pwd`/builds nice ./ct-ng menuconfig
./ct-ng xtensa-esp32s3-linux-uclibcfdpic
popd
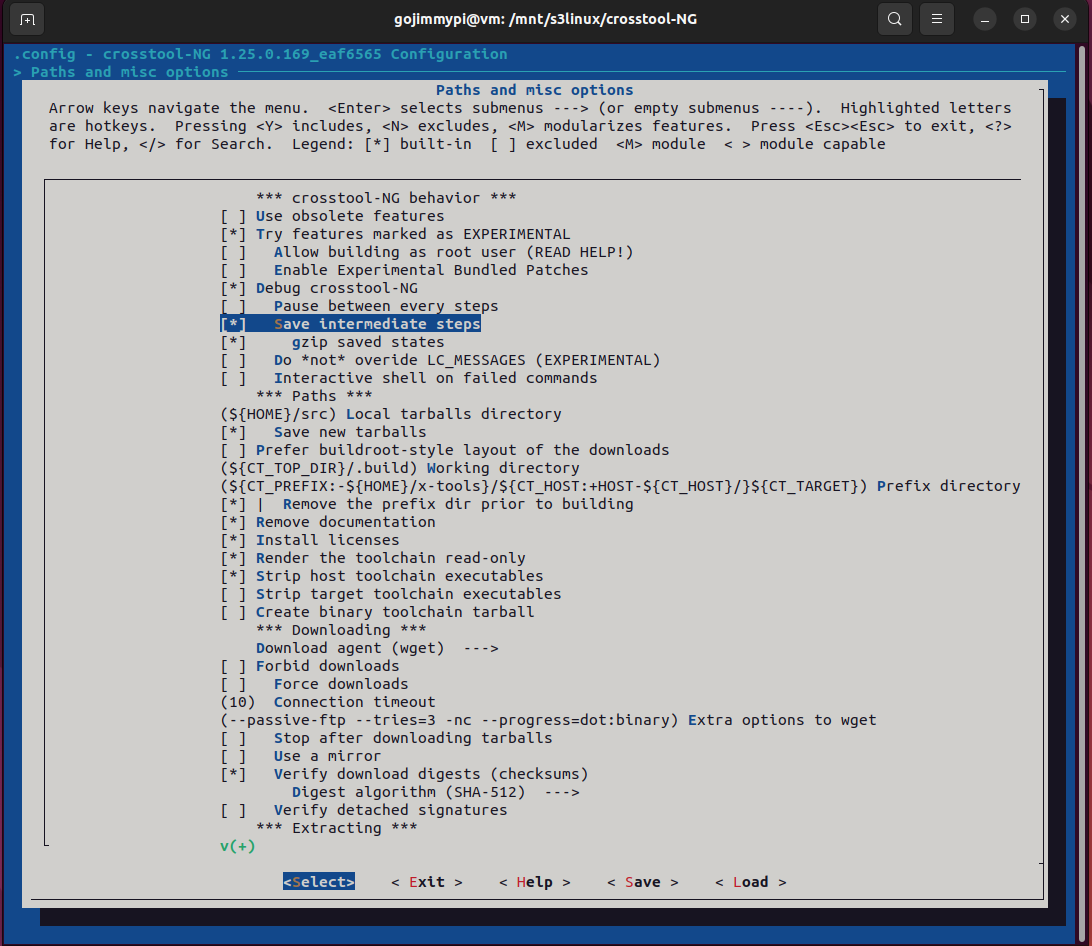
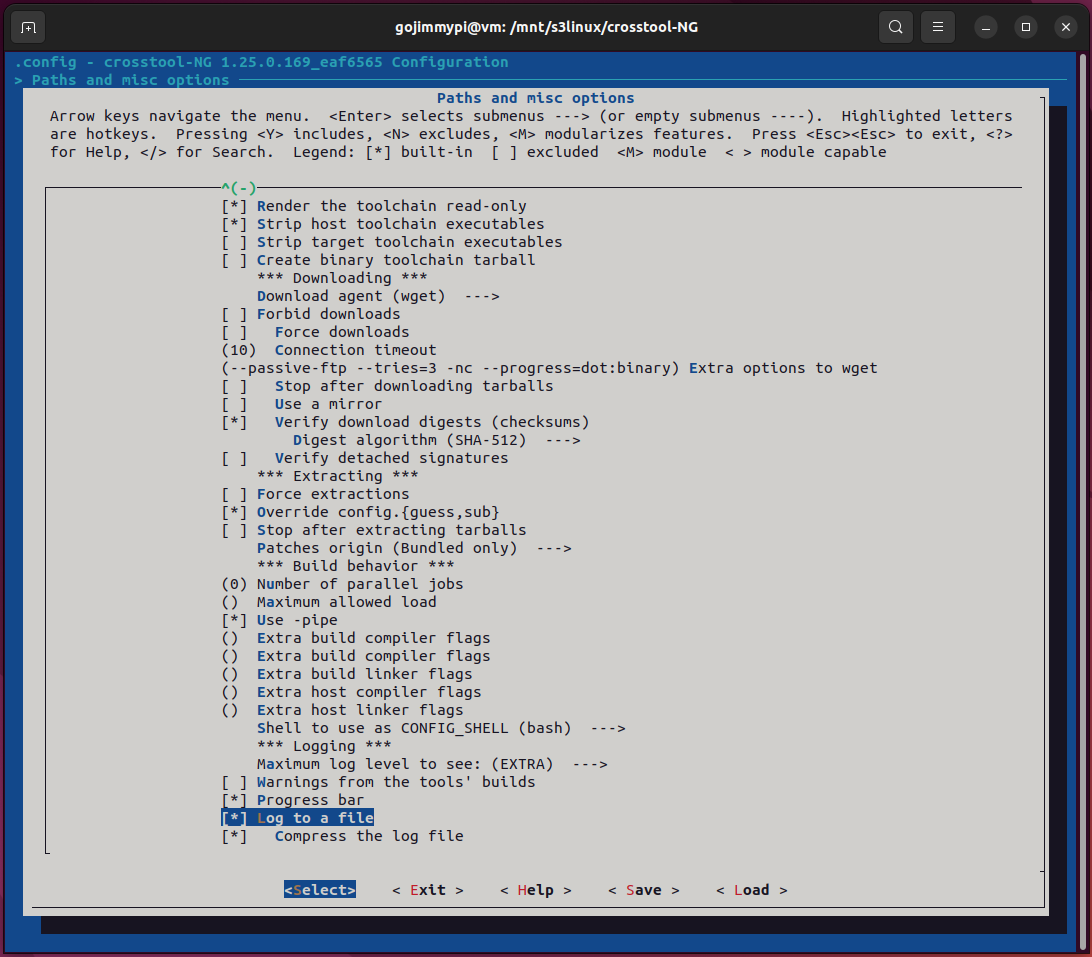
Optional crosstool-ng menuconfig
The Paths and misc options - save intermediate steps is very helpful, particularly considering the
length of time that it takes to build the toolchain.
Here are the settings used in this build. Most are defaults, but note some important adjustments.
Note: Debug crosstool-ng, and enable save intermediate steps. Consider also Interactive shell on failed commands.
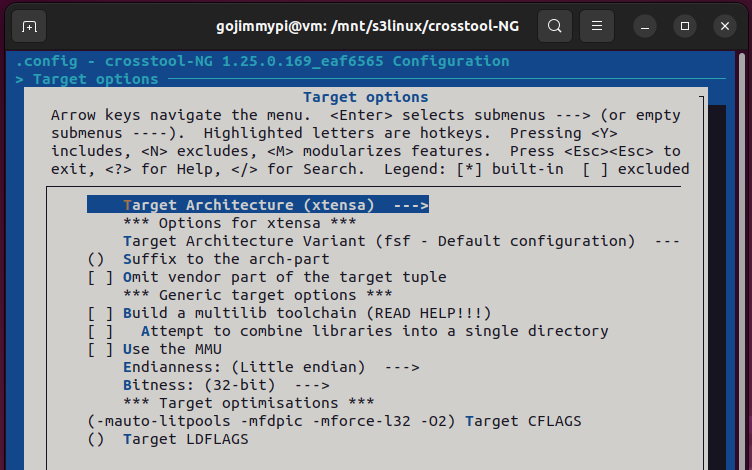
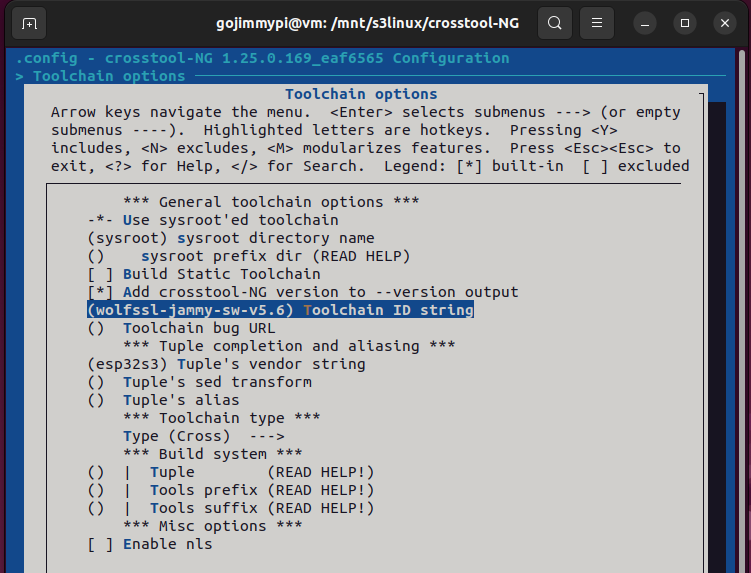
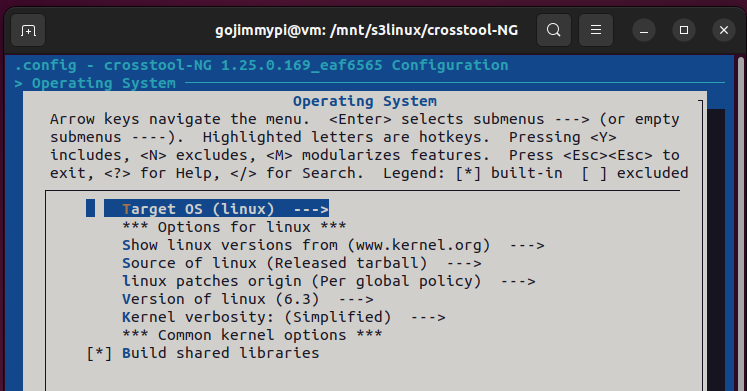
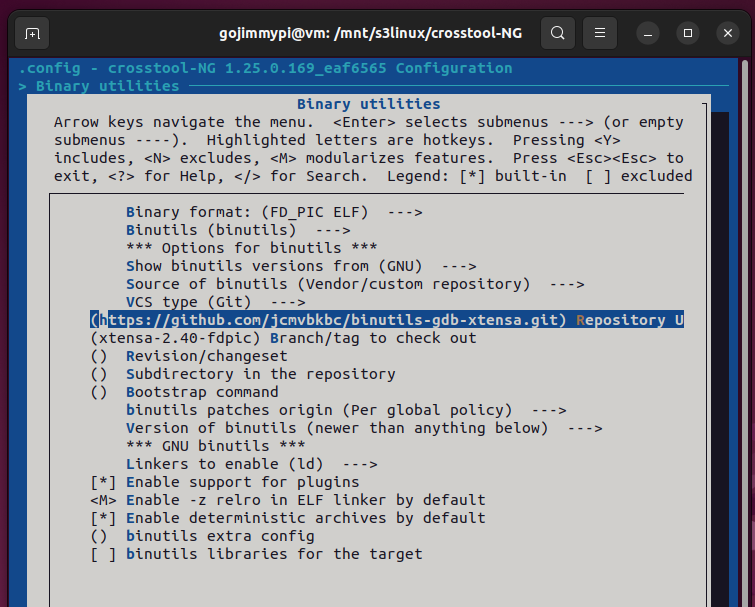
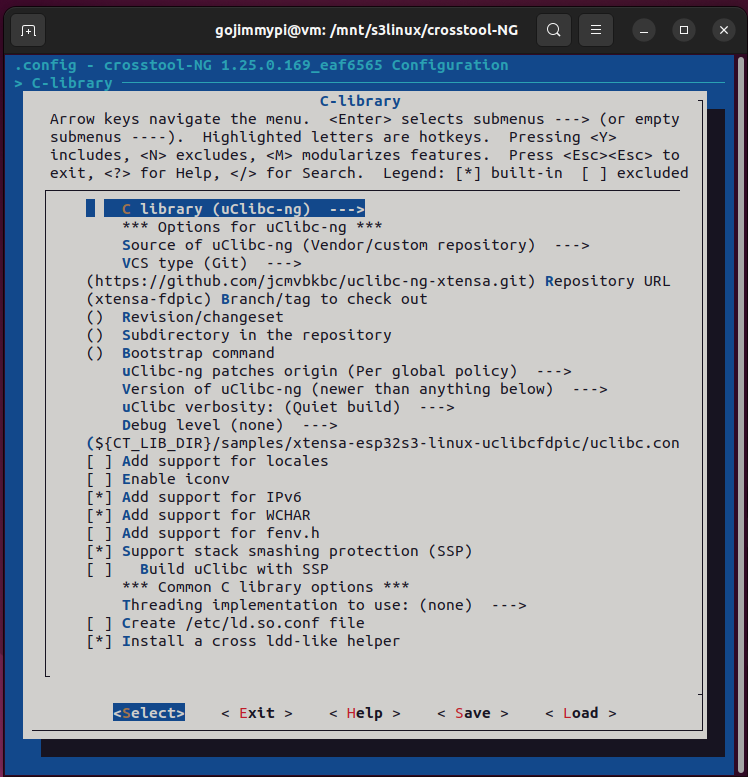
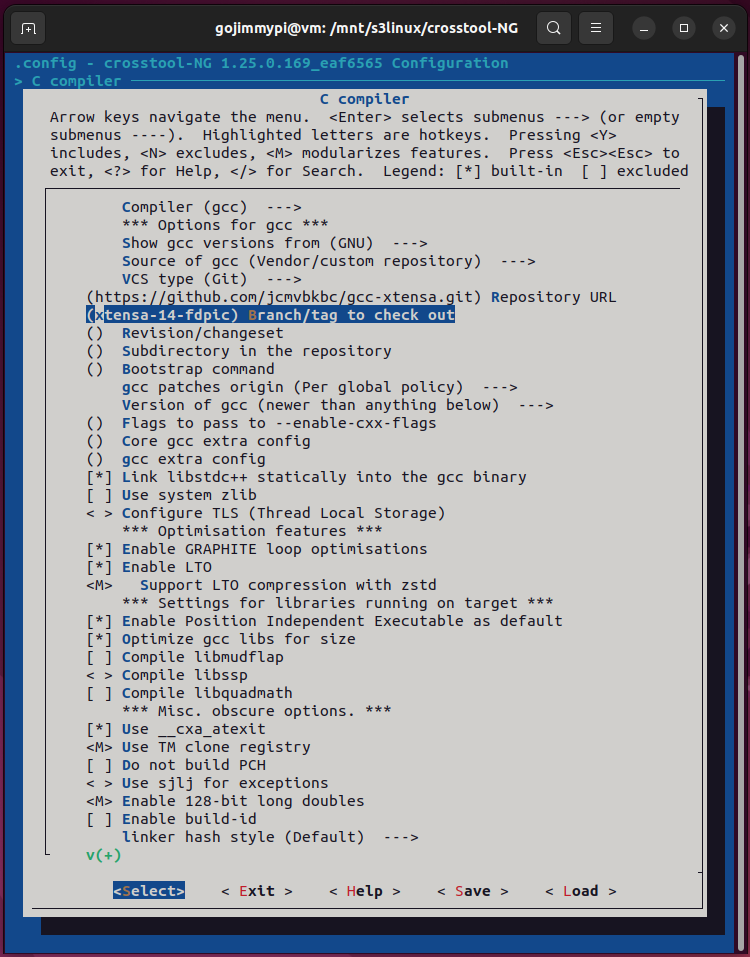
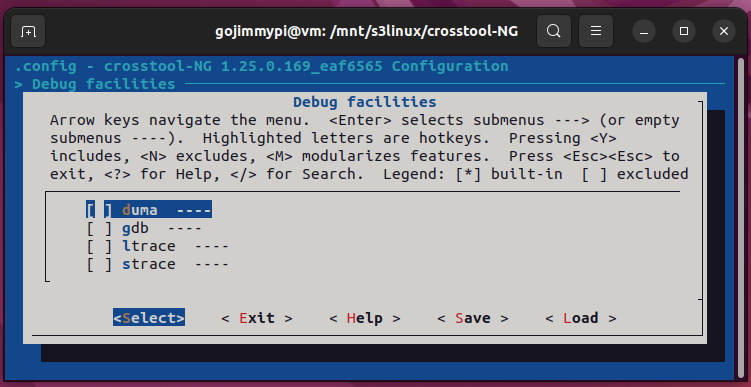
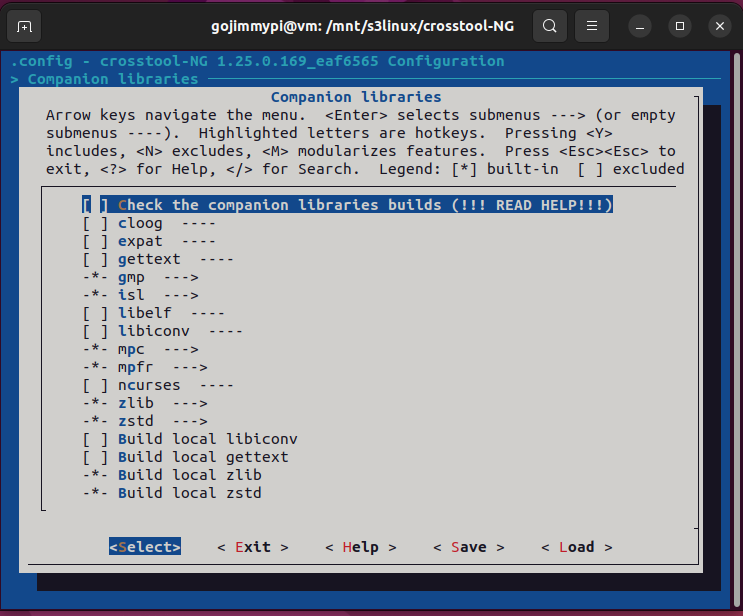
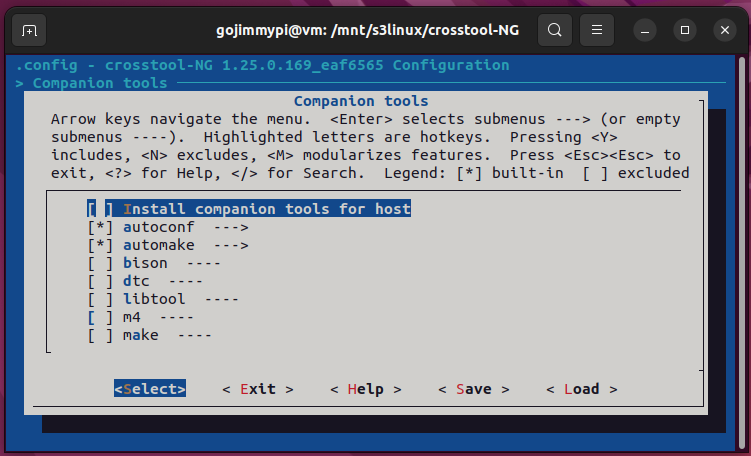
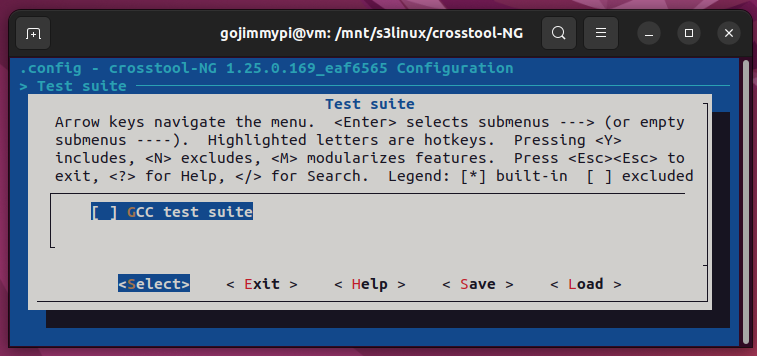
cd /mnt/s3linux
# aka cd ./crosstool-NG
pushd crosstool-NG
# run the menu config
CT_PREFIX=`pwd`/builds nice ./ct-ng menuconfig
# if changes were made abd saved, rebuild xtensa-esp32s3-linux-uclibcfdpic
./ct-ng xtensa-esp32s3-linux-uclibcfdpic
# aka cd .. (but could change if something went horribly wrong in build, so use popd)
popd
Build the toolchain using crosstool-NG
This can take a rather long time.
pushd crosstool-NG
CT_PREFIX=`pwd`/builds nice ./ct-ng build
popd
Optional Clean. This would be VERY RARE to need to rebuild the toolchain:
CT_PREFIX=`pwd`/builds nice ./ct-ng clean
After cleaning, configs are lost. Reset values as needed and run above build.
Edit source: repairs
There was a known minor problem with the source code. Hopefully fixed upstream soon.
Comment out the attribute_hidden decorator on line 114 of sysroot/usr/include/bits/elf-fdpic.h as needed:
elf-fdpic.h:114:17: error: expected ';' before 'void'
Need to comment out the attribute_hidden at the end of the file:
/* attribute_hidden */ void*
__self_reloc (const struct elf32_fdpic_loadmap *map, void ***p, void ***e);
vi /mnt/s3linux/crosstool-NG/builds/xtensa-esp32s3-linux-uclibcfdpic/xtensa-esp32s3-linux-uclibcfdpic/sysroot/usr/include/bits/elf-fdpic.h
The elf-fdpic.h file is refreshed for the build, so be sure to edit it at the right time.
Continue from cc_for_host
If there was an error in elf-fdpic.h as noted above, we can continue from that step, not needing to completely start over.
To see all available steps: CT_PREFIX=pwd/builds nice ./ct-ng list-steps
Here we continue from the cc_for_host step:
CT_PREFIX=`pwd`/builds nice ./ct-ng cc_for_host+
One error is expected at this time
There may still be errors at completion. These are known, but the Checking dynamic linker symlinks
error can be ignored:
[INFO ] Saving state to restart at step 'libc_post_cc'...
[INFO ] =================================================================
[INFO ] Checking dynamic linker symlinks
[EXTRA] Checking dynamic linker for multilib ''
[ERROR] collect2: error: ld returned 1 exit status
[ERROR]
[ERROR] >>
[ERROR] >> Build failed in step 'Checking dynamic linker symlinks'
[ERROR] >> called in step '(top-level)'
[ERROR] >>
[ERROR] >> Error happened in: CT_DoExecLog[scripts/functions@377]
[ERROR] >> called from: CT__FixupLDSO[scripts/functions@1695]
[ERROR] >> called from: CT_IterateMultilibs[scripts/functions@1608]
[ERROR] >> called from: CT_MultilibFixupLDSO[scripts/functions@1761]
[ERROR] >> called from: uClibc_ng_post_cc[scripts/build/libc/uClibc-ng.sh@335]
[ERROR] >> called from: do_libc_post_cc[scripts/build/libc.sh@38]
[ERROR] >> called from: main[scripts/crosstool-NG.sh@697]
Check that the toolchain was properly created.
The following steps assume the xtensa-esp32s3-linux-uclibcfdpic- toolchain was created, above.
To confirm:
cd /mnt/s3linux/
ls crosstool-NG/builds/xtensa-esp32s3-linux-uclibcfdpic/bin -al
There should be a list something like this:
total 413872
drwxrwxr-x 2 gojimmypi gojimmypi 4096 juin 11 01:58 .
drwxrwxr-x 8 gojimmypi gojimmypi 4096 juin 11 01:58 ..
-rwxr-xr-x 1 gojimmypi gojimmypi 5850656 juin 10 23:19 xtensa-esp32s3-linux-uclibcfdpic-addr2line
-rwxr-xr-x 2 gojimmypi gojimmypi 6027872 juin 10 23:19 xtensa-esp32s3-linux-uclibcfdpic-ar
-rwxr-xr-x 2 gojimmypi gojimmypi 8001896 juin 10 23:19 xtensa-esp32s3-linux-uclibcfdpic-as
lrwxrwxrwx 1 gojimmypi gojimmypi 36 juin 11 01:58 xtensa-esp32s3-linux-uclibcfdpic-cc -> xtensa-esp32s3-linux-uclibcfdpic-gcc
-rwxr-xr-x 1 gojimmypi gojimmypi 5795072 juin 10 23:19 xtensa-esp32s3-linux-uclibcfdpic-c++filt
-rwxr-xr-x 1 gojimmypi gojimmypi 7821944 juin 11 01:58 xtensa-esp32s3-linux-uclibcfdpic-cpp
-rwxr-xr-x 1 gojimmypi gojimmypi 5147 juin 10 23:08 xtensa-esp32s3-linux-uclibcfdpic-ct-ng.config
-rwxr-xr-x 1 gojimmypi gojimmypi 126392 juin 10 23:19 xtensa-esp32s3-linux-uclibcfdpic-elfedit
-rwxr-xr-x 2 gojimmypi gojimmypi 7815784 juin 11 01:58 xtensa-esp32s3-linux-uclibcfdpic-gcc
-rwxr-xr-x 2 gojimmypi gojimmypi 7815784 juin 11 01:58 xtensa-esp32s3-linux-uclibcfdpic-gcc-14.0.0
-rwxr-xr-x 1 gojimmypi gojimmypi 147896 juin 11 01:58 xtensa-esp32s3-linux-uclibcfdpic-gcc-ar
-rwxr-xr-x 1 gojimmypi gojimmypi 147744 juin 11 01:58 xtensa-esp32s3-linux-uclibcfdpic-gcc-nm
-rwxr-xr-x 1 gojimmypi gojimmypi 147752 juin 11 01:58 xtensa-esp32s3-linux-uclibcfdpic-gcc-ranlib
-rwxr-xr-x 1 gojimmypi gojimmypi 7179264 juin 11 01:58 xtensa-esp32s3-linux-uclibcfdpic-gcov
-rwxr-xr-x 1 gojimmypi gojimmypi 5622600 juin 11 01:58 xtensa-esp32s3-linux-uclibcfdpic-gcov-dump
-rwxr-xr-x 1 gojimmypi gojimmypi 5656792 juin 11 01:58 xtensa-esp32s3-linux-uclibcfdpic-gcov-tool
-rwxr-xr-x 1 gojimmypi gojimmypi 6399784 juin 10 23:19 xtensa-esp32s3-linux-uclibcfdpic-gprof
-rwxr-xr-x 4 gojimmypi gojimmypi 9111120 juin 10 23:19 xtensa-esp32s3-linux-uclibcfdpic-ld
-rwxr-xr-x 4 gojimmypi gojimmypi 9111120 juin 10 23:19 xtensa-esp32s3-linux-uclibcfdpic-ld.bfd
-rwxr-xr-x 1 gojimmypi gojimmypi 280688896 juin 11 01:58 xtensa-esp32s3-linux-uclibcfdpic-lto-dump
-rwxr-xr-x 2 gojimmypi gojimmypi 5916776 juin 10 23:19 xtensa-esp32s3-linux-uclibcfdpic-nm
-rwxr-xr-x 2 gojimmypi gojimmypi 6657624 juin 10 23:19 xtensa-esp32s3-linux-uclibcfdpic-objcopy
-rwxr-xr-x 2 gojimmypi gojimmypi 9057272 juin 10 23:19 xtensa-esp32s3-linux-uclibcfdpic-objdump
-rwxr-xr-x 2 gojimmypi gojimmypi 6027904 juin 10 23:19 xtensa-esp32s3-linux-uclibcfdpic-ranlib
-rwxr-xr-x 2 gojimmypi gojimmypi 4243264 juin 10 23:19 xtensa-esp32s3-linux-uclibcfdpic-readelf
-rwxr-xr-x 1 gojimmypi gojimmypi 5841216 juin 10 23:19 xtensa-esp32s3-linux-uclibcfdpic-size
-rwxr-xr-x 1 gojimmypi gojimmypi 5853216 juin 10 23:19 xtensa-esp32s3-linux-uclibcfdpic-strings
-rwxr-xr-x 2 gojimmypi gojimmypi 6657624 juin 10 23:19 xtensa-esp32s3-linux-uclibcfdpic-strip
Build the rootfs and kernel image
cd /mnt/s3linux # or wherever you installed your ESP32-S3 Linux toolchain
git clone https://github.com/jcmvbkbc/buildroot -b xtensa-2023.02-fdpic
# this creates the
nice make -C buildroot O=`pwd`/build-xtensa-2023.02-fdpic-esp32s3 esp32s3_defconfig
nice make -C buildroot O=`pwd`/build-xtensa-2023.02-fdpic-esp32s3 menuconfig # adjust external toolchain location to the one built above
nice make -C buildroot O=`pwd`/build-xtensa-2023.02-fdpic-esp32s3
Ensure permissions assigned to flash to serial port
Before flashing, remember that permissions may need to be assigned to the serial port. Those permissions may even need to be reassgned each time the USB device is removed and re-connected to the VM.
A typical error message will look something like this:
/dev/ttyS0 failed to connect: Could not open /dev/ttyS0, the port doesn't exist
Assign permissions like this
sudo chmod 666 /dev/ttyUSB0
Build and flash the bootloader, flash kernel and rootfs images
There’s a main app for the ESP32-S3 that is built as usual with the ESP-IDF. The app is found in the
esp-idf/examples/get-started directory from the jcmvbkbc/esp-idf (linux-5.0.1 branch) and is called
linux_boot:
/* Linux boot Example
This example code is in the Public Domain (or CC0 licensed, at your option.)
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, this
software is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR
CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
*/
#include <stdio.h>
#include "sdkconfig.h"
#include "esp_system.h"
#include "spi_flash_mmap.h"
#include "esp_partition.h"
static const void * IRAM_ATTR map_partition(const char *name)
{
const void *ptr;
spi_flash_mmap_handle_t handle;
esp_partition_iterator_t it;
const esp_partition_t *part;
it = esp_partition_find(ESP_PARTITION_TYPE_ANY, ESP_PARTITION_SUBTYPE_ANY, name);
part = esp_partition_get(it);
if (esp_partition_mmap(part, 0, part->size, SPI_FLASH_MMAP_INST, &ptr, &handle) != ESP_OK)
abort();
return ptr;
}
static void IRAM_ATTR map_flash_and_go(void)
{
const void *ptr0, *ptr;
ptr0 = map_partition("linux");
printf("ptr = %p\n", ptr0);
ptr = map_partition("rootfs");
printf("ptr = %p\n", ptr);
asm volatile ("jx %0" :: "r"(ptr0));
}
void app_main(void)
{
map_flash_and_go();
esp_restart();
}
Here’s how to fetch and build the ESP-IDF part:
cd /mnt/s3linux # or wherever you installed your ESP32-S3 Linux toolchain
git clone https://github.com/jcmvbkbc/esp-idf -b linux-5.0.1
pushd esp-idf
. export.sh
cd examples/get-started/linux_boot
idf.py set-target esp32s3
idf.py build
idf.py flash
popd
Note that the idf.py flash command, (above) flashes only the Linux boot Example for app_main():_
cd /mnt/s3linux
cd ./esp-idf/examples/get-started/linux_boot
idf.py flash
The linux partitions can be flashed separately:
parttool.py write_partition --partition-name linux --input build-xtensa-2023.02-fdpic-esp32s3/images/xipImage
# Flash will be erased from 0x00080000 to 0x002f6fff... (actual size may vary)
parttool.py write_partition --partition-name rootfs --input build-xtensa-2023.02-fdpic-esp32s3/images/rootfs.cramfs
# Flash will be erased from 0x00380000 to 0x00538fff... (actual size may vary)
Optionally flash everything with esptool.py:
python /mnt/s3linux/esp-idf/components/esptool_py/esptool/esptool.py --chip esp32s3 -p /dev/ttyUSB0 -b 115200 --before=default_reset --after=hard_reset write_flash --flash_mode dio --flash_freq 80m --flash_size 8MB 0x0 bootloader/bootloader.bin 0x10000 linux_boot.bin 0x8000 partition_table/partition-table.bin 0x00080000 /mnt/s3linux/extern/xipImage 0x00380000 /mnt/s3linux/extern/rootfs.cramfs
One of the problems that persisted for the longest was this Partition does not exist error:
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "/mnt/s3linux/esp-idf/components/partition_table/parttool.py", line 358, in <module>
main()
File "/mnt/s3linux/esp-idf/components/partition_table/parttool.py", line 351, in main
op(**common_args)
File "/mnt/s3linux/esp-idf/components/partition_table/parttool.py", line 176, in _write_partition
target.write_partition(partition_id, input)
File "/mnt/s3linux/esp-idf/components/partition_table/parttool.py", line 162, in write_partition
self.erase_partition(partition_id)
File "/mnt/s3linux/esp-idf/components/partition_table/parttool.py", line 154, in erase_partition
partition = self.get_partition_info(partition_id)
File "/mnt/s3linux/esp-idf/components/partition_table/parttool.py", line 149, in get_partition_info
raise Exception('Partition does not exist')
Exception: Partition does not exist
I believe the problem was related to a bad partition table. (TODO check & confirm)
Later builds:
This is very important:
cd /mnt/s3linux
export XTENSA_GNU_CONFIG=`pwd`/xtensa-dynconfig/esp32s3.so
echo $XTENSA_GNU_CONFIG
In my case, XTENSA_GNU_CONFIG has this value: /mnt/s3linux/xtensa-dynconfig/esp32s3.so
Build the
cd /mnt/s3linux
nice make -C buildroot O=`pwd`/build-xtensa-2023.02-fdpic-esp32s3
Updating config
cd /mnt/s3linux
nice make -C buildroot O=`pwd`/build-xtensa-2023.02-fdpic-esp32s3 esp32s3_defconfig
Adding binaries to /opt/
Place any extra files in /mnt/s3linux/build-xtensa-2023.02-fdpic-esp32s3/target/opt, despite
the warning message:
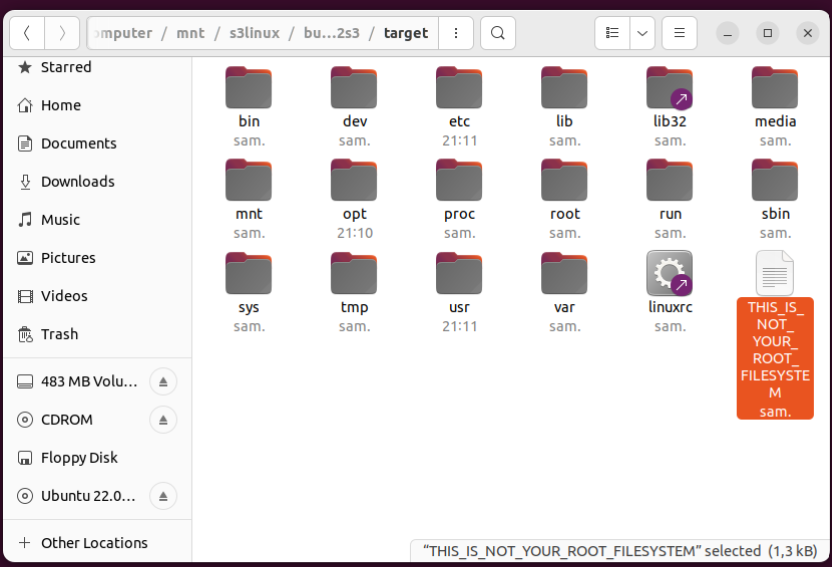
Yes, even though there’s a file that is named THIS_IS_NOT_YOUR_ROOT_FILESYSTEM, placing files in that
directory’s /opt subdirectory will end up included in the rootfs.cramfs binary that is flashed
onto the ESP32-S3. Read the contents on that file for further details.
Additionally, placing files in that directory, and then running make does not require any sort of clean
operation for the new file to be included:
nice make -C buildroot O=`pwd`/build-xtensa-2023.02-fdpic-esp32s3
Building for remote target:
In order to create a custom program to run on the embedded Xtensa linux, the app needs to be cross compiled. At this time there’s no toolchain in the embedded device itself.
The most common error message is undefined reference to __self_reloc’`, such as this:
/mnt/s3linux/crosstool-NG/builds/xtensa-esp32s3-linux-uclibcfdpic/lib/gcc/xtensa-esp32s3-linux-uclibcfdpic/14.0.0/../../../../xtensa-esp32s3-linux-uclibcfdpic/bin/ld: /mnt/s3linux/crosstool-NG/builds/xtensa-esp32s3-linux-uclibcfdpic/xtensa-esp32s3-linux-uclibcfdpic/sysroot/usr/lib/crt1.o: in function `_start':
(.text+0x10): undefined reference to `__self_reloc'
/mnt/s3linux/crosstool-NG/builds/xtensa-esp32s3-linux-uclibcfdpic/lib/gcc/xtensa-esp32s3-linux-uclibcfdpic/14.0.0/../../../../xtensa-esp32s3-linux-uclibcfdpic/bin/ld: BFD (crosstool-NG 1.25.0.169_eaf6565 - wolfssl-jammy-sw-v5.6) 2.40.50.20230424 assertion fail /mnt/s3linux/crosstool-NG/.build/xtensa-esp32s3-linux-uclibcfdpic/src/binutils/bfd/elf32-xtensa.c:2699
collect2: fatal error: ld terminated with signal 11 [Segmentation fault], core dumped
compilation terminated.
Solution: don’t forget the -mfdpic parameter when calling gcc (or more specifically: xtensa-esp32s3-linux-uclibcfdpic-gcc).
Consider this case of Hello World:
main.c:
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
void main() {
printf("wow\n");
}
Compile like this:
$CC -mfdpic -mforce-l32 main.c -o HelloWorld
The toolchain could also be added to your path:
export PATH=/mnt/s3linux/crosstool-NG/builds/xtensa-esp32s3-linux-uclibcfdpic/bin:$PATH
Add HelloWorld to /mnt/s3linux/build-xtensa-2023.02-fdpic-esp32s3/target/opt
cp HelloWorld /mnt/s3linux/build-xtensa-2023.02-fdpic-esp32s3/target/opt/HelloWorld
partition table:
## Label type ST Offset Length
nvs, data, nvs, 0x0000a000, 0x00005000
phy_init, data, phy, 0x0000f000, 0x00001000
factory, app, factory, 0x00010000, 0x00040000
linux, 0x40, 0x0, 0x00080000, 0x00300000
rootfs, 0x40, 0x1, 0x00380000, 0x00480000
Flash with parttool.py:
parttool.py write_partition --partition-name linux --input build-xtensa-2023.02-fdpic-esp32s3/images/xipImage
parttool.py write_partition --partition-name rootfs --input build-xtensa-2023.02-fdpic-esp32s3/images/rootfs.cramfs
Build wolfSSL
Ensure the toolchain is in the path. (see above)
cd /mnt/s3linux
export XTENSA_GNU_CONFIG=`pwd`/xtensa-dynconfig/esp32s3.so # make sure this environment variable is set for all commands involving building or using the toolchain
# change to the directory where wolfSSL will be cloned, (e.g. your `~/workspace/` or in this case, `/mnt/c/test`)
cd /mnt/c/test/
git clone https://github.com/wolfSSL/wolfssl.git wolfssl-xtensa
cd wolfssl-xtensa
./autogen.sh
# host was arm-non-eabi
./configure \
--host=xtensa-esp32s3-linux-uclibcfdpic \
CC=xtensa-esp32s3-linux-uclibcfdpic-gcc \
AR=xtensa-esp32s3-linux-uclibcfdpic-ar \
STRIP=xtensa-esp32s3-linux-uclibcfdpic-strip \
RANLIB=xtensa-esp32s3-linux-uclibcfdpic-ranlib \
--prefix=/mnt/s3linux/crosstool-NG/builds/xtensa-esp32s3-linux-uclibcfdpic \
CFLAGS="-mfdpic -mforce-l32 -DHAVE_PK_CALLBACKS -DWOLFSSL_USER_IO -DNO_WRITEV" \
--disable-filesystem --enable-fastmath \
--disable-shared
make
make check # (optional, but highly recommended
Note that when on the target ESP32 Linux environment, is not using --disable-shared for wolfSSL,
that the /opt shared libraries will need to be added to the path. (although not yet working). Here’s an example config:
./configure \
--host=xtensa-esp32s3-linux-uclibcfdpic \
CC=xtensa-esp32s3-linux-uclibcfdpic-gcc \
AR=xtensa-esp32s3-linux-uclibcfdpic-ar \
STRIP=xtensa-esp32s3-linux-uclibcfdpic-strip \
RANLIB=xtensa-esp32s3-linux-uclibcfdpic-ranlib \
--prefix=/mnt/s3linux/build-xtensa-2023.02-fdpic-esp32s3/target/opt \
--libdir=/opt/lib \
CPPFLAGS="-I./" \
CFLAGS=" -mfdpic -mforce-l32 " \
" -DTIME_T_NOT_64BIT -DNO_WRITEV -DHAVE_PK_CALLBACKS " \
" -DWOLFSSL_USER_IO -DWOLFSSL_USER_SETTINGS -DDEBUG_WOLFSSL " \
" -DTFM_NO_ASM -DALT_ECC_SIZE"
None of these work for shared embedded library yet:
export PATH=/opt/lib:$PATH
export LD_LIBRARY_PATH=/opt/lib
export LD_RUN_PATH=/opt/lib
For example:
/opt # ./benchmark
sh: can't execute './benchmark': No such file or directory
another test with user_settings:
./configure \
--host=xtensa-esp32s3-linux-uclibcfdpic \
CC=xtensa-esp32s3-linux-uclibcfdpic-gcc \
AR=xtensa-esp32s3-linux-uclibcfdpic-ar \
STRIP=xtensa-esp32s3-linux-uclibcfdpic-strip \
RANLIB=xtensa-esp32s3-linux-uclibcfdpic-ranlib \
--prefix=/mnt/s3linux/crosstool-NG/builds/xtensa-esp32s3-linux-uclibcfdpic \
CFLAGS="-mfdpic -DHAVE_PK_CALLBACKS -DWOLFSSL_USER_IO -DNO_WRITEV -DWOLFSSL_USER_SETTINGS -DDEBUG_WOLFSSL -DWOLFSSL_SMALL_STACK -DTFM_NO_ASM" \
--disable-filesystem --enable-fastmath \
--disable-shared
output prefeix /mnt/s3linux/build-xtensa-2023.02-fdpic-esp32s3/target/opt
./configure \
--host=xtensa-esp32s3-linux-uclibcfdpic \
CC=xtensa-esp32s3-linux-uclibcfdpic-gcc \
AR=xtensa-esp32s3-linux-uclibcfdpic-ar \
STRIP=xtensa-esp32s3-linux-uclibcfdpic-strip \
RANLIB=xtensa-esp32s3-linux-uclibcfdpic-ranlib \
--prefix=/mnt/s3linux/build-xtensa-2023.02-fdpic-esp32s3/target/opt \
CFLAGS="-mfdpic -DHAVE_PK_CALLBACKS -DWOLFSSL_USER_IO -DNO_WRITEV -DWOLFSSL_USER_SETTINGS -DDEBUG_WOLFSSL -DWOLFSSL_SMALL_STACK -DTFM_NO_ASM" \
--disable-filesystem --disable-all \
--disable-shared
tiny footprint –disable-fpecc CFLAGS=’-DALT_ECC_SIZE’ –disable-dh –disable-ecc –disable-rsa –disable-sp-asm –disable-sha384 –disable-sha512 –disable-sha –disable-sha224 –disable-md5 -DWOLFSSL_STATIC_PSK -DMAX_PSK_ID_LEN=32 -DWOLFSSL_MAX_MTU=300
./configure –disable-all –enable-tls13 –enable-psk –disable-dh –disable-ecc –disable-rsa –enable-sp-asm –disable-sha384 –disable-sha512 –disable-sha –disable-sha224 –disable-md5 CFLAGS=”-DWOLFSSL_STATIC_PSK -DMAX_PSK_ID_LEN=32 -DWOLFSSL_MAX_MTU=300”
tiny, tiny
./configure \
--host=xtensa-esp32s3-linux-uclibcfdpic \
CC=xtensa-esp32s3-linux-uclibcfdpic-gcc \
AR=xtensa-esp32s3-linux-uclibcfdpic-ar \
STRIP=xtensa-esp32s3-linux-uclibcfdpic-strip \
RANLIB=xtensa-esp32s3-linux-uclibcfdpic-ranlib \
--prefix=/mnt/s3linux/build-xtensa-2023.02-fdpic-esp32s3/target/opt \
CFLAGS="-mfdpic -DNO_WRITEV -DWOLFSSL_USER_SETTINGS -DDEBUG_WOLFSSL -DTFM_NO_ASM -DALT_ECC_SIZE" \
--disable-filesystem --disable-all \
--disable-shared --enable-smallstack --enable-psk --enable-sha --disable-fpecc --disable-ecc --disable-rsa --disable-sp-asm --disable-sha384 --disable-sha512 --disable-sha224 --disable-md5
make CC=/mnt/s3linux/crosstool-NG/builds/xtensa-esp32s3-linux-uclibcfdpic/bin/xtensa-esp32s3-linux-uclibcfdpic-gcc
export CC=/mnt/s3linux/crosstool-NG/builds/xtensa-esp32s3-linux-uclibcfdpic/bin/xtensa-esp32s3-linux-uclibcfdpic-gcc
Resources, Inspiration, Credits, References, and Other Links:
Espressif
- Getting Started with ESP-IDF
- Espressif Devkits
- Application Startup Flow
- ESP32-S3 Series Data Sheet
- esp_partition_mmap fails with partitions larger than 3MB (IDFGH-107) #1184
- espressif/xtensa-overlays
- Flashing Firmware
- esp32-wifi-lib Please open source this library
- ESP32-WROOM-32e pinout change
wolfSSL
- PDF wolfSSL Manual
- Building wolfSSL
- wolfSSL for Espressif
- wolfSSL ESP32 Examples
- wolfSSL espressif docs
- wolfSSL Espressif ESP32-C3 RISC-V Support
- wolfSSH examples for Espressif on ESP32 or ESP8266
- wolfssl-examples
- Reducing wolfssl memory usage
- True Random vs. Pseudorandom Number Generation
- Implementing Hardware Cryptographic Support in wolfCrypt
- youtube.com/@Wolfssl/videos
jcmvbkbc
- linux-xtensa
- Booting linux on ESP32s3
- static void IRAM_ATTR map_flash_and_go(void)
- linux-xtensa #5
- linux-xtensa #5 (GPIO)
VMware
ESP32DE
Other references
- ARM FDPIC Toolchain and ABI see also video.
- Putty download
- esp32.com Run linux on the ESP32?
- Lyontek PSRAM
- PSRAM,
- PSRAM