Create an embedded UART SSH Server on the Adafruit Huzzah ESP8266. Securely connect to Tx/Rx serial pins from your network via WiFi. Source code is available on GitHub. See also the ESP32 SSH Server project, which includes a wired ethernet option with the ENC28J60.
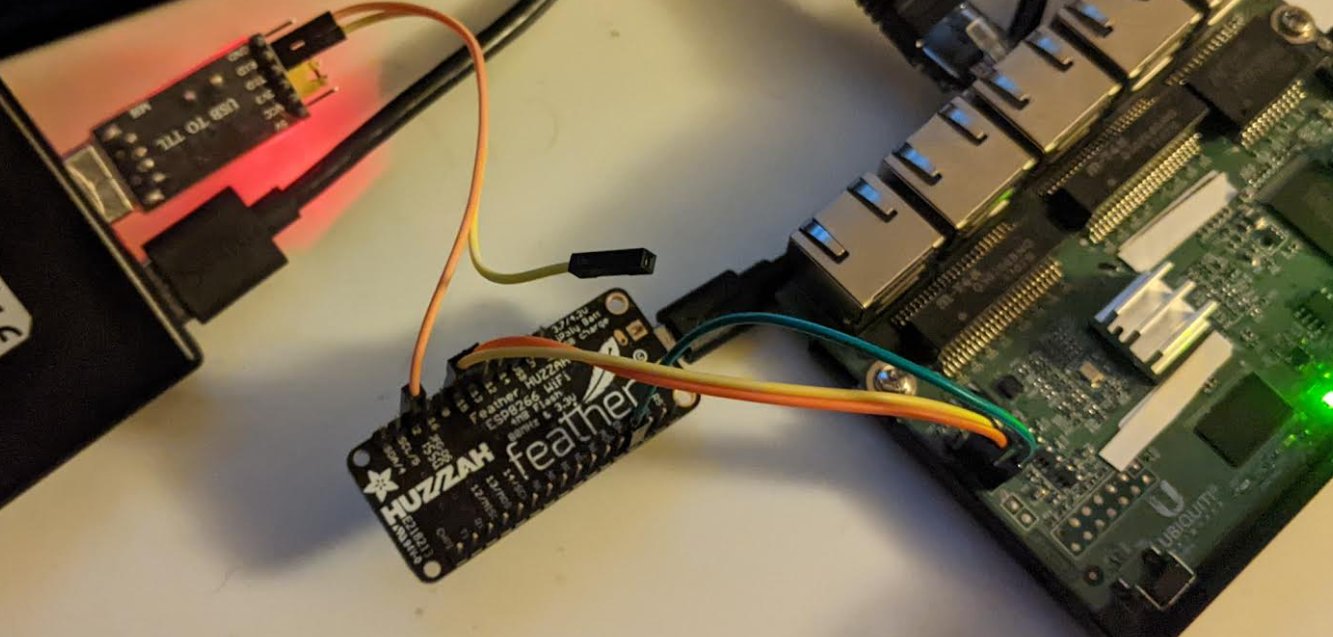
Much of the complexity of this project turned out to be the shell game of UARTs.
When all is said and done, we’ll have the ESP8266 console on UART1
and the Tx/Rx pins of our target device connected to UART0 via (UART #2).
The challenge here was although there are 3 hardware UARTs on the ESP8266, only 2 can be active and usuable at any given time.
Of the 2 active UARTs, only one can have both Tx and Rx. Only UART0 and UART2 have both Tx and Rx.
Also: UART1 can only transmit. There’s no RXD1:
| Actual UART | Progammatic Name | Tx | Rx |
|---|---|---|---|
| UART #0 | UART_NUM_0 | TXD0 = GPIO 1 = Tx | RXD0 = GPIO 3 = Rx |
| UART #1 | UART_NUM_1 | TXD1 = GPIO 2 = D4 | N/A |
| UART #2 | UART_NUM_0 | TXD2 = GPIO 15 = D7 | RXD2 = GPIO 13 = D8 |
Line #3: UART_NUM_0 for UART #2 is not a typo.
There’s no UART2, no programmatic UART_NUM_2 in code.
The USB port is normally connected to UART0. (which could be either UART #0 or UART #2)
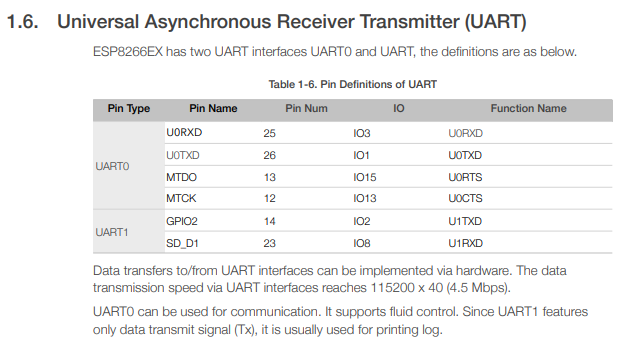
See also the ESP8266 Technical Reference, page 3 (PDF page 11), section 1.6:
See also the note on the next page of the technical reference document:
By default, UART0 outputs some printed information when the device is powered on and booting up. The baud rate of the printed information is relevant to the frequency of the external crystal oscillator. If the frequency of the crystal oscillator is 40 MHz, then the baud rate for printing is 115200; if the frequency of the crystal oscillator is 26 MHz, then the baud rate for printing is 74880. If the printed information exerts any influence on the functionality of the device, it is suggested to block the printing during the power-on period by changing (U0TXD,U0RXD) to (MTDO,MTCK).
So we need two UART swaps: one to configure the console output prior to compile, another at runtime.
UART #0 can be swapped with UART #2 by using uart_enable_swap(); after initialization:
// Configure parameters of an UART driver,
// communication pins and install the driver
uart_config_t uart_config = {
.baud_rate = BAUD_RATE,
.data_bits = UART_DATA_8_BITS,
.parity = UART_PARITY_DISABLE,
.stop_bits = UART_STOP_BITS_1,
.flow_ctrl = UART_HW_FLOWCTRL_DISABLE
};
uart_param_config(UART_NUM_0, &uart_config);
/* Install UART driver, and get the queue. */
uart_driver_install(UART_NUM_0, BUF_SIZE * 2, BUF_SIZE * 2, 100, &uart0_queue, 0);
/* swap GPIO pins 1,3 with 15,13 */
uart_enable_swap();
Note that after the swap, UART #2 will still be known as UART0 in code! The difference is now
UART0 will be using different pins.
When swapping UART #0 and UART #2, in our case, we don’t want the USB traffic to be seen on the
external UART for our SSH Server. But we do want to be able to see diagnostic messages that
are normally viewed on the USB port. The ESPLOG default output is configured with the ESP-IDF make menuconfig
The other swap is done prior to compiling.
It is important to ensure the ESP8266 console is NOT routed to UART0 (the default), but instead to UART.
The issue is the second UART only has Tx pin available as confirmed on ESP8266 forum.
The sdkconfig
for the command-line ESP-IDF, and
the VisualGDB config
are already setup to do this.
To manually check, use make menuconfig:
Component config --->
ESP8266-specific --->
UART for console output ---> Custom
UART peripheral to use for console output(0-1) ---> (UART1)
or in some cases:
Common ESP-related --->
UART for console output (Custom) ---> Custom
UART peripheral to use for console output (0-1) --->(UART1)
It is important that GPIO15 is not pulled high at boot time.
If the target Tx pin is pulled high, or the Tx/Rx pins are reversed, the ESP8266 will not boot properly.
Remove the target Tx/Rx pins during programming as needed. The Ubuiquiti EdgeReouter-X
did not need to have them disconnected for this example.
Building
The project was developed in Visual Studio with the VisualGDB extension. Just open the solution file in the examples/ESP8266-SSH-Server directory. Right-click the project and “Build…”:
Alternatively, the code can be built via the RTOS ESP-IDF for ESP8266
ESP8266 Toolchain
Install the latest ESP8266 Toolchain.
To use a dual Windows/Linux (WSL) option, consider a shared directory such as C:\ESP8288\esp\
which would be /mnt/c/ESP8266/esp/ in WSL.
Note there may be an old version of wolfSSL in ESP8266_RTOS_SDK\components\esp-wolfssl that should be deleted.
mkdir -p /mnt/c/ESP8266/esp/
cd /mnt/c/ESP8266/esp/
git clone --recursive https://github.com/espressif/ESP8266_RTOS_SDK.git
export IDF_PATH="/mnt/c/ESP8266/esp/ESP8266_RTOS_SDK/"
# Optional section if python pip needs to be installed
# see https://pip.pypa.io/en/stable/installation/
wget https://bootstrap.pypa.io/get-pip.py
# or for Python 2.7
# wget https://bootstrap.pypa.io/pip/2.7/get-pip.py
# install pip if needed
python -m pip install --user -r $IDF_PATH/requirements.txt
# download the Espressif xtensa compiler
curl --output xtensa-lx106-elf-gcc8_4_0-esp-2020r3-linux-amd64.tar.gz https://dl.espressif.com/dl/xtensa-lx106-elf-gcc8_4_0-esp-2020r3-linux-amd64.tar.gz
# unzip Espressif xtensa compiler
tar -xzf xtensa-lx106-elf-gcc8_4_0-esp-2020r3-linux-amd64.tar.gz
# tell the environment where to find the xtensa compiler
export PATH="$PATH:/mnt/c/ESP8266/esp/xtensa-lx106-elf/bin"
# delete the old version of wolfSSL
rm -r ./ESP8266_RTOS_SDK/components/esp-wolfssl
Quick Start
For convenience ONLY, there’s a static stale copy of wolfSSL components.
DO NOT USE those static components for anything other than this demo. To ensure proper security,
please install the latest code into the Espressif components directory and
delete your local copy found in examples/Espressif-component-static.
The Makefile can also have these lines removed:
EXTRA_COMPONENT_DIRS = ../Espressif-component-static/
CPPFLAGS += -DWOLFSSL_STALE_EXAMPLE=YES
CFLAGS += -DWOLFSSL_STALE_EXAMPLE=YES
WSL Quick Start, use the ESPPORT with make:
# change to whatever directory you use for projects
cd /mnt/c/workspace/
git clone https://github.com/gojimmypi/wolfssh.git
cd ./wolfssh
git checkout ESP8266_Development
cd ./examples/ESP8266-SSH-Server
# Reminder that WSL USB devices are called /dev/ttySNN and not /dev/TTYUSBn
# For example, on Windows, COM15 is ttyS15 in WSL
make flash ESPPORT=/dev/ttyS15
BUT Note that there’s a STALE version of the wolfSSL component for convenience only! For proper security, the most recent code should always be used:
# fetch the ESP8266-SSH-Server example
cd /mnt/c/workspace
git clone https://github.com/gojimmypi/wolfssh/tree/ESP8266_Development/examples/ESP8266-SSH-Server
cd /mnt/c/workspace/wolfSSH/examples/ESP8266-SSH-Server
# optional; existing settings should be appropriate
# make menuconfig
make
See also:
esp_err_t uart_enable_swap(void)
Connection
Connect device Rx pin to TXD2 = GPIO 15;
device Tx pin to RXD2 = GPIO 13; connect GND.
Troubleshooting
Here are some potential solutions to issues that may be encountered.
No response from serial device during SSH session.
Confirm the Tx and Rx pins are connected correctly.
Make sure there’s a ground connection.
Note the Ubuiquiti EdgeReouter-X does apparently have some logic built in to disable the serial TTY port when an excess of garbage characters (failed logins?) are detected. So if it seems that all should be working, but isn’t - check that the target device serial port is actually responsive with a direct connect via Putty.
No rule to make target
A message such as No rule to make target typically indicated the environment has not been
set properly.
0 $ make flash ESPPORT=/dev/ttyS15
make: *** No rule to make target 'flash'. Stop.
To resolve the ‘No rule to make target’, set environment variables as discussed above:
export PATH="$PATH:/mnt/c/ESP8266/esp/xtensa-lx106-elf/bin"
If the error continues to occur, make sure there’s a Makefile. The wolfSSH/.gitignore excludes Makefiles for some reason.
Could not open port ‘COM[n]’: WindowsError(5, ‘Access is denied.’)
An error like this, although intimidating and long, typically means something else is using the COM port. Check for running instances of Putty, etc.
esptool.py v2.4.0
Flashing binaries to serial port COM15 (app at offset 0x10000)...
esptool.py v2.4.0
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "C:/SysGCC/esp8266/rtos-sdk/v3.4/components/esptool_py/esptool/esptool.py", line 3035, in <module>
_main()
File "C:/SysGCC/esp8266/rtos-sdk/v3.4/components/esptool_py/esptool/esptool.py", line 3028, in _main
main()
File "C:/SysGCC/esp8266/rtos-sdk/v3.4/components/esptool_py/esptool/esptool.py", line 2736, in main
esp = chip_class(args.port, initial_baud, args.trace)
File "C:/SysGCC/esp8266/rtos-sdk/v3.4/components/esptool_py/esptool/esptool.py", line 212, in __init__
self._port = serial.serial_for_url(port)
File "C:/SysGCC/esp8266/mingw32/lib/python2.7/site-packages/serial/__init__.py", line 88, in serial_for_url
instance.open()
File "C:/SysGCC/esp8266/mingw32/lib/python2.7/site-packages/serial/serialwin32.py", line 62, in open
raise SerialException("could not open port {!r}: {!r}".format(self.portstr, ctypes.WinError()))
serial.serialutil.SerialException: could not open port 'COM15': WindowsError(5, 'Access is denied.')
make: *** [/rtos-sdk/v3.4/components/esptool_py/Makefile.projbuild:76: flash] Error 1
--------------------------
Command exited with code 2
Fatal error: wolfssl/options.h: No such file or directory
If a wolfSSL not found error like this is encountered:
In file included from /mnt/c/workspace/wolfssh-gojimmypi-ESP32/examples/ESP8266-SSH-Server/main/uart_helper.c:27:
/mnt/c/workspace/wolfssh-gojimmypi-ESP32/examples/ESP8266-SSH-Server/main/ssh_server.h:41:10: fatal error: wolfssl/options.h: No such file or directory
#include <wolfssl/options.h>
^~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
compilation terminated.
make[1]: *** [/mnt/c/ESP8266/esp/ESP8266_RTOS_SDK/make/component_wrapper.mk:292: uart_helper.o] Error 1
make: *** [/mnt/c/ESP8266/esp/ESP8266_RTOS_SDK//make/project.mk:571: component-main-build] Error 2
Be sure to install both the wolfSSL and wolfSSH components.
For example, into: C:\ESP8266\esp\ESP8266_RTOS_SDK\components.
Be sure to install wolfSSL component first as the wolfSSH component has dependencies.
c:
cd C:\workspace\wolfssl-gojimmypi\IDE\Espressif\ESP-IDF
.\setup_win.bat C:\ESP8266\esp\ESP8266_RTOS_SDK\
c:
cd C:\workspace\wolfssh-gojimmypi-ESP32\ide\Espressif\ESP-IDF
.\setup_win.bat C:\ESP8266\esp\ESP8266_RTOS_SDK\
Or, if you are using the VisualGDB extension for Visual Studio and want to compile from WSL command-line:
.\setup_win.bat C:\SysGCC\esp8266\rtos-sdk\v3.4
Where is the wolfSSL config file?
As noted in wolfssl/pull/5077:
The method of uncommenting a line in settings.h is outdated.
Most people use user_settings.h / WOLFSSL_USER_SETTINGS or ./configure CFLAGS="-DFLAG" now.
The user_settings.h is typically found in components\wolfssl\include
fatal error: soc/dport_reg.h: No such file or directory
An error such as this in esp32-crypt.h:
/mnt/c/ESP8266/esp/ESP8266_RTOS_SDK/components/wolfssh/wolfssl/wolfcrypt/port/Espressif/esp32-crypt.h:38:10: fatal error: soc/dport_reg.h: No such file or directory
#include "soc/dport_reg.h"
^~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
compilation terminated.
make[1]: *** [/mnt/c/ESP8266/esp/ESP8266_RTOS_SDK/make/component_wrapper.mk:292: main.o] Error 1
make: *** [/mnt/c/ESP8266/esp/ESP8266_RTOS_SDK//make/project.mk:571: component-main-build] Error 2
This error indicates the wrong target device is selected (ESP8266 needed vs ESP32 found )
Check your config.
Other Stuff
There’s this junhuanchen/esp-idf-software-serial with these compile errors:
Severity Description Project File Line
Error implicit declaration of function 'gpio_pad_select_gpio'; did you mean 'gpio_set_direction'? EmbeddedProject9 C:\Users\gojimmypi\source\repos\EmbeddedProject9\main\sw_serial.h 39
Error implicit declaration of function 'esp_cpu_get_ccount'; did you mean 'soc_get_ccount'? EmbeddedProject9 C:\Users\gojimmypi\source\repos\EmbeddedProject9\main\sw_serial.h 69
Error unknown type name 'portMUX_TYPE'; did you mean 'portBASE_TYPE'? EmbeddedProject9 C:\Users\gojimmypi\source\repos\EmbeddedProject9\main\sw_serial.h 81
Error 'portMUX_INITIALIZER_UNLOCKED' undeclared (first use in this function) EmbeddedProject9 C:\Users\gojimmypi\source\repos\EmbeddedProject9\main\sw_serial.h 81
Error macro "portENTER_CRITICAL" passed 1 arguments, but takes just 0 EmbeddedProject9 C:\Users\gojimmypi\source\repos\EmbeddedProject9\main\sw_serial.h 82
Error 'portENTER_CRITICAL' undeclared (first use in this function) EmbeddedProject9 C:\Users\gojimmypi\source\repos\EmbeddedProject9\main\sw_serial.h 82
Error macro "portEXIT_CRITICAL" passed 1 arguments, but takes just 0 EmbeddedProject9 C:\Users\gojimmypi\source\repos\EmbeddedProject9\main\sw_serial.h 113
Error 'portEXIT_CRITICAL' undeclared (first use in this function) EmbeddedProject9 C:\Users\gojimmypi\source\repos\EmbeddedProject9\main\sw_serial.h 113
Error unknown type name 'portMUX_TYPE'; did you mean 'portBASE_TYPE'? EmbeddedProject9 C:\Users\gojimmypi\source\repos\EmbeddedProject9\main\sw_serial.h 142
Error 'portMUX_INITIALIZER_UNLOCKED' undeclared (first use in this function) EmbeddedProject9 C:\Users\gojimmypi\source\repos\EmbeddedProject9\main\sw_serial.h 142
Error macro "portENTER_CRITICAL" passed 1 arguments, but takes just 0 EmbeddedProject9 C:\Users\gojimmypi\source\repos\EmbeddedProject9\main\sw_serial.h 143
Error 'portENTER_CRITICAL' undeclared (first use in this function) EmbeddedProject9 C:\Users\gojimmypi\source\repos\EmbeddedProject9\main\sw_serial.h 143
Error macro "portEXIT_CRITICAL" passed 1 arguments, but takes just 0 EmbeddedProject9 C:\Users\gojimmypi\source\repos\EmbeddedProject9\main\sw_serial.h 162
Error 'portEXIT_CRITICAL' undeclared (first use in this function) EmbeddedProject9 C:\Users\gojimmypi\source\repos\EmbeddedProject9\main\sw_serial.h 162
Error unknown type name 'wSerial'; did you mean 'SwSerial'? EmbeddedProject9 C:\Users\gojimmypi\source\repos\EmbeddedProject9\main\main.c 156
A software serial UART was not part of this project, although it would be interesting if multiple target devices might be desired on each Espressif board.
Resources, Inspiration, Credits, and Other Links
- Adafruit Feather HUZZAH with ESP8266
- Adafruit Huzzah ESP8266 Pinout v1.2
- Espressif ESP8266 Technical Reference
- Espressif GitHub ESP8266_RTOS_SDK
- ESP8266 forum Second UART
- Espressif FAQ UART0 and UART1
- GitHub ESP8266_RTOS_SDK issue 667, example
- Docs ESP8266 RTOS SDK Programming Guide - UART
- GitHub ESP8266_RTOS_SDK/components/esp8266/driver/uart.c
- Arduino esp8266 serial notes
- VisualGDB Debugging ESP8266 firmware with the UART GDB Stub
- GitHub ESP8266_RTOS_SDK/components/esp8266/driver/gpio.c
- Non-Arduino plieningerweb/esp8266-software-uart
- Arduino GitHub issue Enabling UART2 for the NodeMCU?